EYE :-
The postion of Human Eye’s in Frontal in Location.
Binocular vision can be done by human. (Binocular vision means we can see easily one object from both Eye’s in one time.)
- These are the most sensory part of our body.
- These are protected by :-
- Orbit(Bones protection{by the help of 8 type of bone’s})
- Eye’s Lashes [Upper Lashes(moveable) and Lower Lashes(inmoveable)]
- Conjuctiva
- Eye Infection
- Pink Eye’s
- Eye flew
- Conjuctivitie’s
- Eye Infection
- 3rd Eye lid (Nictitating membrane and Plicae Semilunaris) is vestigel [not functioning]
Structure of Human Eye :-
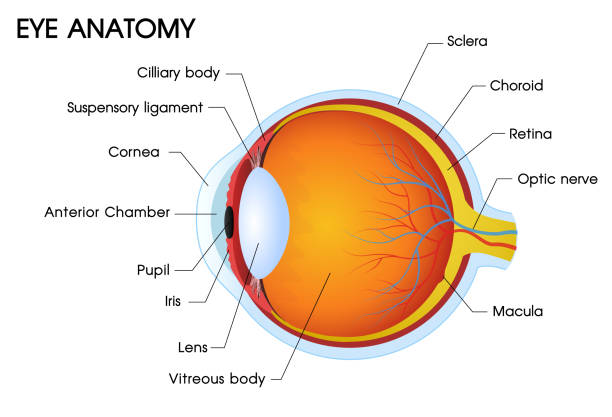
Hollow boll and filled with fluid
1. Made up of 3 Layer’s
-
- First layer/Outer Layer is Tunica Fibrosa.
- Second layer
- Third Layer is Tunica Nervosa
Tunica Fibrosa :-
Tunica Fibrosa [1. Sclera{Backside(5/6)} 2. Cornea{Frontside(1/6)}]
[Note:-Cornea Get oxygen direct from atmosphere]
. Tunica fibrosa is help to maintain the shape of the Eye
. Sclera can make Posterior part is 5/6 part.(White Par)
. Cornea can make Anterior part and they can make 1/6 part and they will be transparent.(The most successfull transplant cornea because their is no blood supply in cornea.)
Second Layer :-
It is made up of Blue Colour.
This is second layer and middle layer of Eye this is called Tunica pigmentosa and Tunica vascular.
Melanin pigment was present .
Melanin can absorb the extra light that was enter’s in the Eye.
Pigmentosa can also divided into 3 part’s.
- Choroid
- Ciliary Body
- Ciliary processes
- Ciliary Muscle’s
- Iris (Coloured part of the Human Eye)
The gap between two Iris is known as pupil.
Through the pupil light can enter’s into the eye Pupil’s size can regulated by the Iris.
Third Layer :-
This is known as Tunica Nervosa / Neurosensory / Retina.
In this layer neuron’s are present.
In this layer 3 Cell’s are present
- Ganglionic
- Bipolar
- Photo receptor Cell’s
- Rode’s
- Cone’s
Yellow spot (made up of photo receptor’s Cell’s ) was present just behind the pupil at the centre and the other name of Yellow Spot is Mocula Lukia.
The arrangement of the cell’s are Ganglionic then Bipolar at middle and the photo receptor Cell’s are present at last.
At the yellow spot the ganglonic and bipolar Cell’s are absent.
Photo receptor’s Cell’s are two type’s
- Rode’s (Rode’s are used in night time / dimness)
- Cone’s (Cone’s are used in day time in brightness)
Len’s :-
The len’s are present just behind the iris.
The len’s will be connected by suspensory ligament’s.
By the help suspensory ligament can change the shape and size.
Ciliary Muscle and suspensory ligament can change the focal length of len’s.
Blind Spot :-
Blind spot is that place from that place the nerves are present / rise.
These nerve are known as Optic Nerve.
Optic nerve is the Second cranial nerve.
That is sensory in Nature.
Rode’s and cone’s both are absent on blind spot .
Between len’s and cornea the fluid was present that is known as Aqueous(Fluid) Humor’s(Watery).
Aqueous Humor’s was secrated by ciliary processes
Aqueous Humor’s is responsible for maintain the pressure in the Eye.
Behind the len’s the fluid is also present that is known as Vitreous(Jelly type) Humor’s(Watery)
Difference between Rod Cell’s and Cone Cell’s :-
Rod Cell’s :-
- Cylindrically-shaped cell’s in the retina that respond to dim Light.
- Outer sigment is rod Shaped.
- Comparatively long.
- Contain’s approximately 90 million’s Cell’s.
- Distributes through the Retina.
- Involved in peripheral vision.
- Only a single type occur in the retina.
- Responsible for non-chromatic vision.
- Contain Rhodopsin
- More sensitive and responsible for night vision.
- Several Rod Cell’s connect to a single bipolar Cell’s.
- Possess a poor acuity(Sharpness.)
- Regenerative power is high.
Cone Cell’s :-
- Cone-Shaped , visual receptor cell’s in the retina that are sensitive to bright light and colour.
- Outer segment is Cone-Shaped.
- Comparatively Long.
- Contain approximately 6 million cell’s.
- Mainly occur in the fovea
- Can only tetct the image in the centre of the retina.
- Three types occure in the retina
- Responsible for coloured vision.
- Contain photopsin /Iodopsin.
- Have a poor sensitivity and require bright light for vision.
- One Cone Cell’s connected to one bipolar cell
- Possess a higher acuity
- Regenerative power is low.
Mechanism Of Vision :-
Mechanism of vision occur’s in two part’s
- Focusing Part.
- Biochemical Part.
Focusing Part :-
- Light must focus on Yellow Spot.
- Refraction Conjuctiva.
- ⇓
- Cornea (maximum refraction).
- ⇓
- Aqueous Humous.
- ⇓
- Len’s .
- ⇓
- Vitreous Humous.
- ⇓
- Yellow Spot.
Part’s Involved :-
- Len’s (Thinner)
- Suspensory Ligament’s(Contract)
- Ciliary Muscle’s (Relax)
- Iris(Contrict)
- Pupil(When Dilate then more light Enter.)
Biochemical Part :-
When fall’s on yellow spot which contain PRC (Cones)
⇓
Contain Visual → 1)Iodopsin(visual voilet) → Retinal + Photopsin → Red
→ Green
→Blue
Red + Green + Blue = Equal Stimulation of all 3 cone’s can create White sensation
Pigments(photo-sensitive) → 2)Rhodopsin(visual purple) → Retinal + Scotopsin
↓
Undergo Biochemical Change’s
On moving from bright light to dim light :-
- We suffer from temporary blindness
- Bright light has degenerated Rhodopsin(Bleaching)
- For dim light → we require Rhodopsin.
- Rhodopsin ⇌ Retinal + Scotopsin

